Researchers awarded DOD grant
 Orthopaedic researchers at Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center have been awarded a $2.24 million four-year grant from the U. S. Department of Defense (DOD) to study the use of keratin gel in the regeneration of damaged peripheral nerves, those in the hands, arms and feet.
Orthopaedic researchers at Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center have been awarded a $2.24 million four-year grant from the U. S. Department of Defense (DOD) to study the use of keratin gel in the regeneration of damaged peripheral nerves, those in the hands, arms and feet.Categories: Research & Discovery, University Announcements

 Up to 65 percent of runners sustain an overuse injury each year. Wake Forest researchers, funded by a $600,000 grant from the U. S. Army, plan to find out why.
Up to 65 percent of runners sustain an overuse injury each year. Wake Forest researchers, funded by a $600,000 grant from the U. S. Army, plan to find out why. David Weinstein, a professor of political science and one of Wake Forest’s most prolific scholars in the humanities, often inhabits two intellectual worlds. As he moves between them, he’s extending Wake Forest’s academic reach to Israel, Germany, Italy and England.
David Weinstein, a professor of political science and one of Wake Forest’s most prolific scholars in the humanities, often inhabits two intellectual worlds. As he moves between them, he’s extending Wake Forest’s academic reach to Israel, Germany, Italy and England. What do Indian food and filmmaking tell us about America? Under the guidance of Assistant Professor Sandya Hewamanne, students Bridget Bagel and Meenu Krishnan conducted research, which they presented at the Conference on South Asia.
What do Indian food and filmmaking tell us about America? Under the guidance of Assistant Professor Sandya Hewamanne, students Bridget Bagel and Meenu Krishnan conducted research, which they presented at the Conference on South Asia.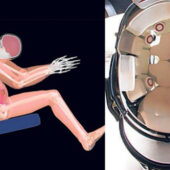 Identifying and diagnosing sports concussions quicker is at the heart of a collaborative effort between the Virginia Tech-Wake Forest University Center for Injury Biomechanics and Toyota Motor Corp.
Identifying and diagnosing sports concussions quicker is at the heart of a collaborative effort between the Virginia Tech-Wake Forest University Center for Injury Biomechanics and Toyota Motor Corp. Thanks in part to efforts of School of Law professors and students, some local high school students recently visited college campuses in the Washington, D.C., and Philadelphia areas. The trip was designed to enhance their level of enthusiasm for the college selection process.
Thanks in part to efforts of School of Law professors and students, some local high school students recently visited college campuses in the Washington, D.C., and Philadelphia areas. The trip was designed to enhance their level of enthusiasm for the college selection process. In Tina Boyer's first-year seminar class, students meet dragons, giants and other mythological creatures.
In Tina Boyer's first-year seminar class, students meet dragons, giants and other mythological creatures. Alcoholic energy drinks are under fire after reports of unsafe behaviors, especially among college students. These actions are encouraging to associate professor Mary Claire O’Brien, M.D., who conducted groundbreaking research into the dangers of the drinks.
Alcoholic energy drinks are under fire after reports of unsafe behaviors, especially among college students. These actions are encouraging to associate professor Mary Claire O’Brien, M.D., who conducted groundbreaking research into the dangers of the drinks. Junior Amy Liang, through her work with Wake Forest’s Campus Kitchen, has seen the problems of the hungry and homeless. Last summer, she conducted a research project, which included creating a documentary film, to raise awareness of the issues.
Junior Amy Liang, through her work with Wake Forest’s Campus Kitchen, has seen the problems of the hungry and homeless. Last summer, she conducted a research project, which included creating a documentary film, to raise awareness of the issues.  Students in John Pickel's lab have completed video art installations that will be exhibited Nov. 16-27 at the Student Art Gallery (START Gallery) in Reynolda Village.
Students in John Pickel's lab have completed video art installations that will be exhibited Nov. 16-27 at the Student Art Gallery (START Gallery) in Reynolda Village.